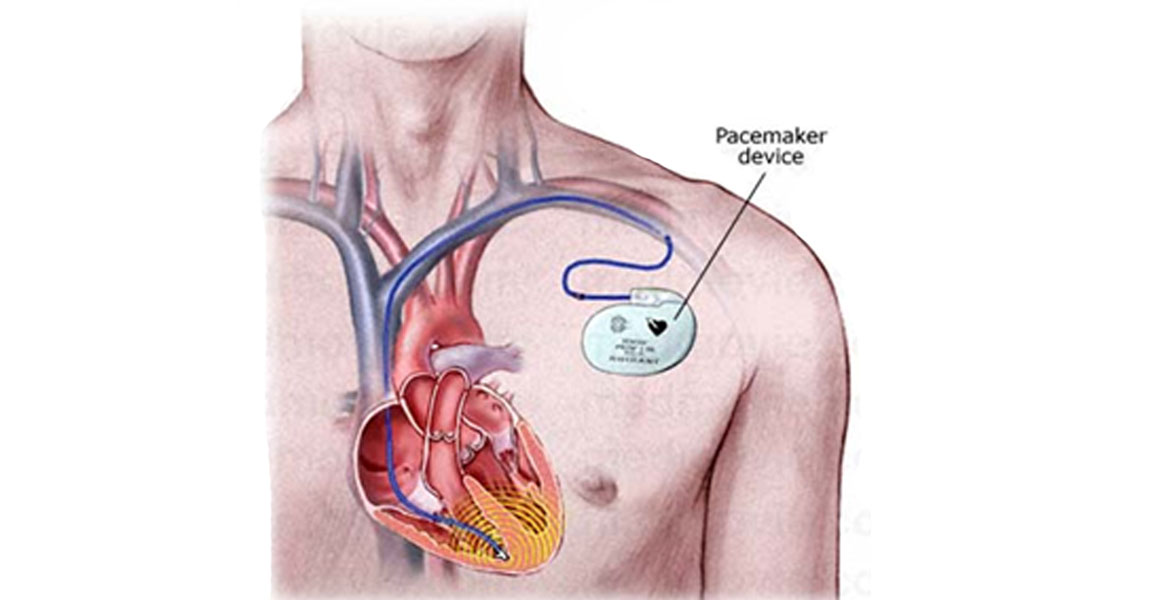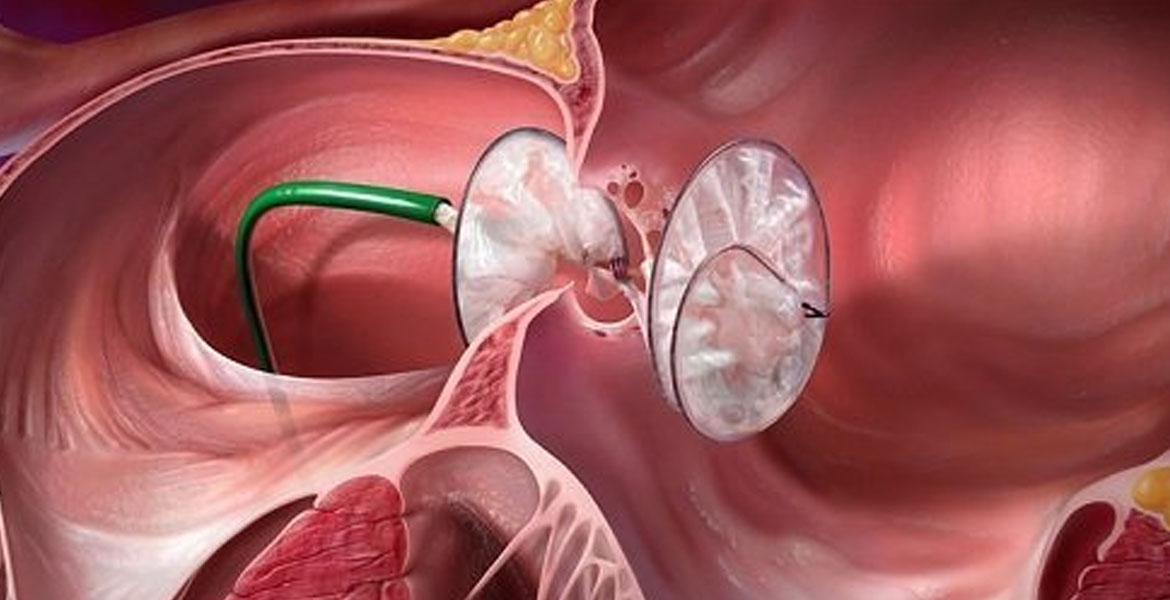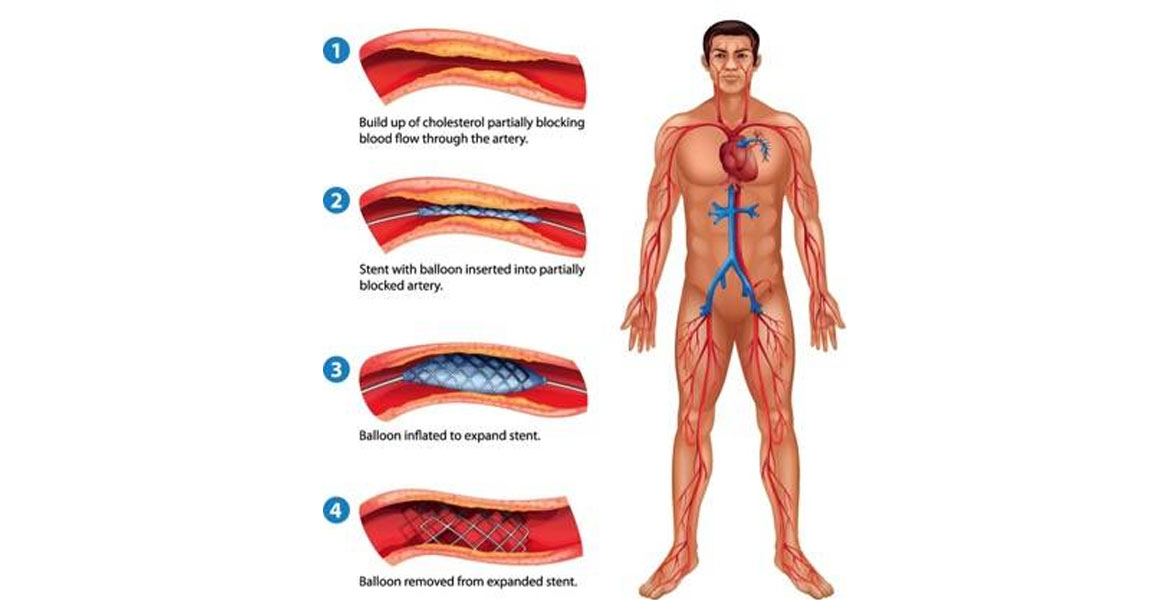
Coronary angioplasty, also defined as percutaneous coronary involvement, is a methodology used to access clogged arteries of the heart. Angioplasty uses a tiny balloon catheter that is implanted into an obstructed blood vessel to help widen and enhance the flow of blood to your heart. Angioplasty is often integrated with a small wire mesh tube called a stent. The stent helps to keep the artery open, reducing its chance of narrowing again. Most stents are coated with drugs to help keep your artery open (drug-eluting stents). Bare metal stents may infrequently be used.

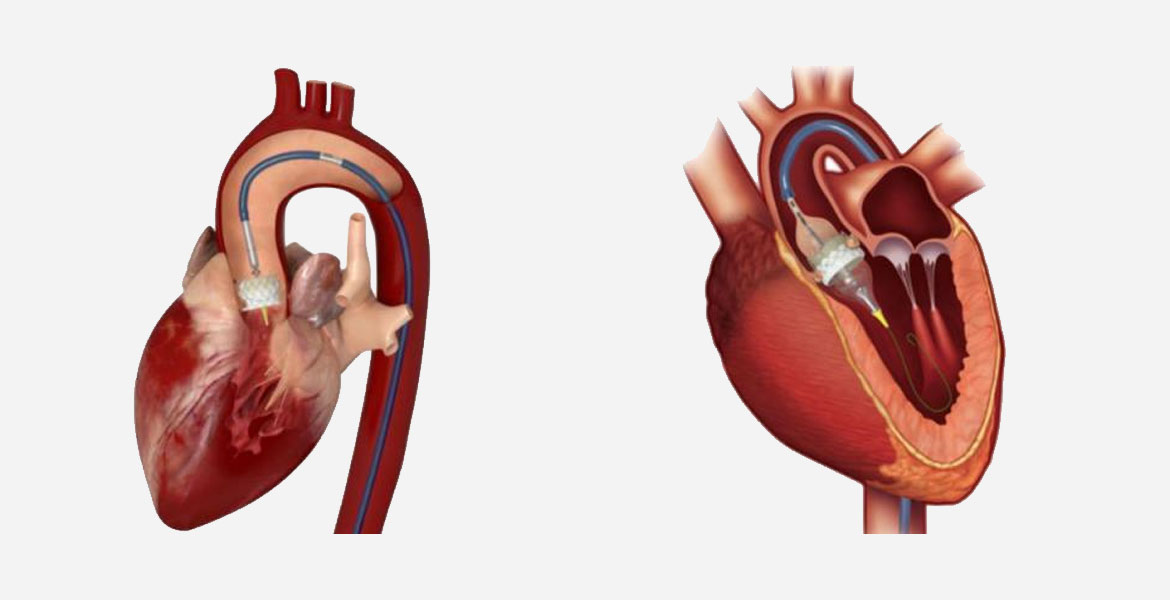
.jpg)